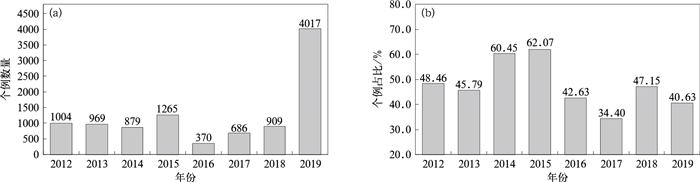
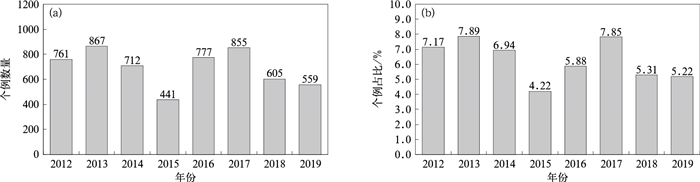
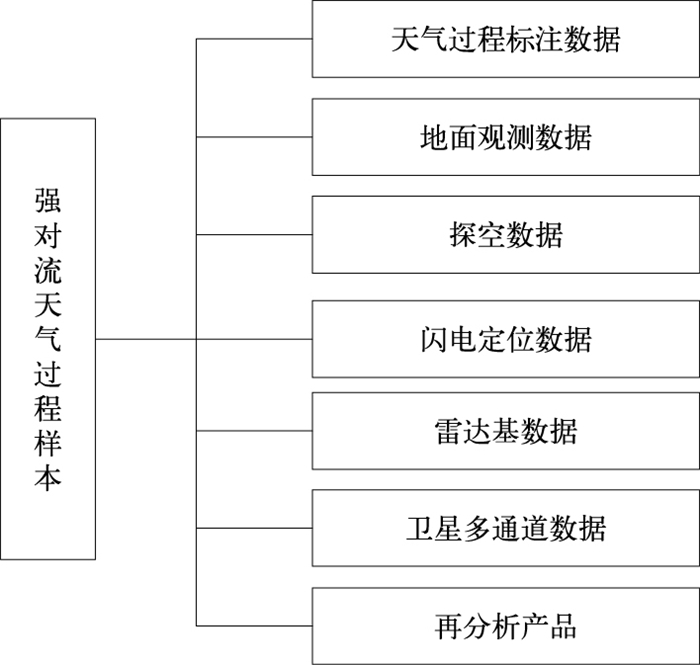
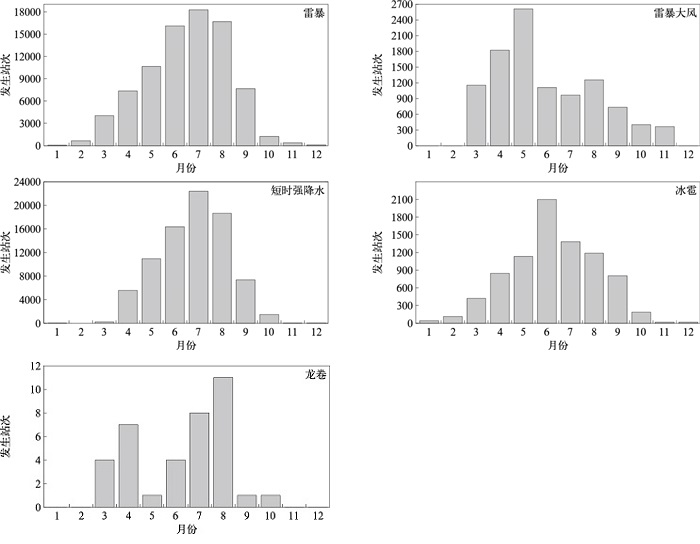
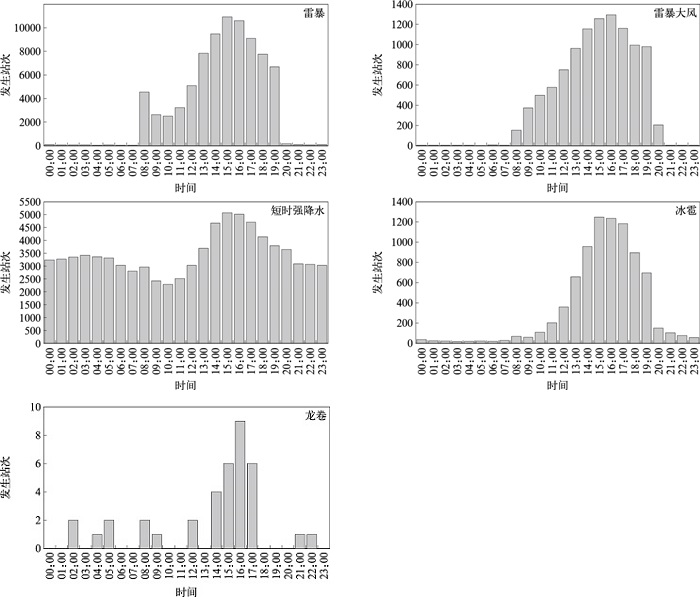
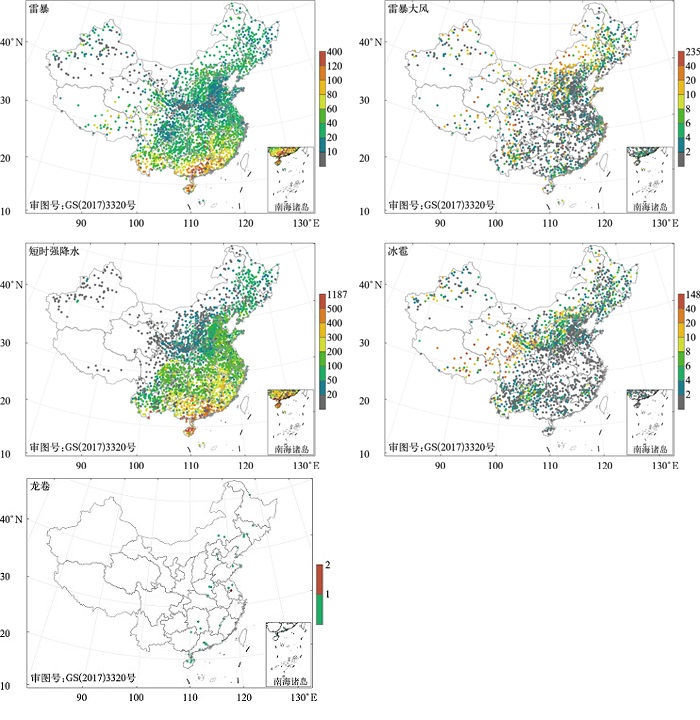
|
[1]
|
|
|
[2]
|
Hitchens N M, Brooks H E. Evaluation of the storm prediction center's day 1 convective outlooks. Wea Forecasting, 2012, 27(6): 1580-1585. doi: 10.1175/WAF-D-12-00061.1 |
|
[3]
|
Gagne D J, McGovern A, Haupt S E, et al. Storm-based probabilistic hail forecasting with machine learning applied to convection-allowing ensembles. Wea Forecasting, 2017, 32(5): 1819-1840. doi: 10.1175/WAF-D-17-0010.1 |
|
[4]
|
Sun J, Cao Z, Li H, et al. Application of artificial intelligence technology to numerical weather prediction. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2021, 32(1): 1-11. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210101 |
|
[5]
|
Perler D, Marchand O. A study in weather model output postprocessing: Using the boosting method for thunderstorm detection. Wea Forecasting, 2009, 24(1): 211-222. doi: 10.1175/2008WAF2007047.1 |
|
[6]
|
Lagerquist R, McGovern A, Smith T. Machine learning for real-time prediction of damaging straight-line convective wind. Wea Forecasting, 2017, 32(6): 2175-2193. doi: 10.1175/WAF-D-17-0038.1 |
|
[7]
|
|
|
[8]
|
|
|
[9]
|
Mecikalski, John R, Williams, et al. Probabilistic 0-1-h convective initiation nowcasts that combine geostationary satellite observations and numerical weather prediction model data. J Appl Meteorol Climatol, 2015, 54(5): 1039-1059. doi: 10.1175/JAMC-D-14-0129.1 |
|
[10]
|
Shi X J, Chen Z R, Wang H, et al. Convolutional LSTM network: A Machine Learning Approach for Precipitation Nowcasting//Proc 28th Int Conf on NIPS, 2015: 802-810.
|
|
[11]
|
Han F, Long M S, Li Y A, et al. The application of recurrent neural network to nowcasting. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2019, 30(1): 61-69. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20190106 |
|
[12]
|
Shi X J, Gao Z H, Lausenl L, et al. Deep Learning for Precipitation Nowcasting: A Benchmark and New Model//Proc 31st Conf on NIPS, 2017: 5617-5627.
|
|
[13]
|
Jing J, Li Q, Peng X. MLC-LSTM: Exploiting the spatiotemporal correlation between multi-level weather radar echoes for echo sequence extrapolation. Sensors, 2019, 19(18): 3988-4008. doi: 10.3390/s19183988 |
|
[14]
|
Zhou K H, Zheng Y, Li B, et al. Forecasting different types of convective weather: A deep learning approach. J Meteor Res, 2019, 33(5): 797-809. doi: 10.1007/s13351-019-8162-6 |
|
[15]
|
|
|
[16]
|
Liu B J, Zhang Y P, Li Z J, et al. An objective hailstorm labeling algorithm based on ground observation. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2021, 32(1): 78-90. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20210107 |
|
[17]
|
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y |
|
[18]
|
Dai A, Chang A X, Savva M, et al. ScanNet: Richly-Annotated 3D Reconstructions of Indoor Scenes//IEEE Conf on CVPR, 2017: 2432-2443.
|
|
[19]
|
Hersbach H, Bell B, Berrisford P, et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc, 2020, 146(730): 1999-2049. doi: 10.1002/qj.3803 |
|
[20]
|
Zheng Y G, Zhou K H, Sheng J, et al. Advances in techniques of monitoring, forecasting and warning of severe convective weather. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2015, 26(6): 641-657. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150601 |
|
[21]
|
China Meteorological Administration. Specifications for Surface Meteorological Observation. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2003.
|
|
[22]
|
Wang H, Li Y, Song L L, et al. Comparison of characteristics and environmental factors of thunderstorm gales over the Sichuan-Tibet Region. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2020, 31(4): 435-446. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20200406 |
|
[23]
|
|
|
[24]
|
|
|
[25]
|
|
|
[26]
|
|
|
[27]
|
|
|
[28]
|
Ruan X, Xiong A Y, Hu K X, et al. Correcting geopotential height errors of some mandatory levels of Chinese historic radiosonde observations. J Appl Meteor Sci, 2015, 26(3): 257-267. doi: 10.11898/1001-7313.20150301 |
|
[29]
|
|
|
[30]
|
|
|
[31]
|
|
|
[32]
|
|
|
[33]
|
|
|
[34]
|
Jiang Y. Meteorological Radar Data Quality Control Study and Application. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, 2013.
|
|
[35]
|
China Meteorological Administration. Yearbook of Meteorological Disasters in China(2013-2019). Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2013-2019.
|




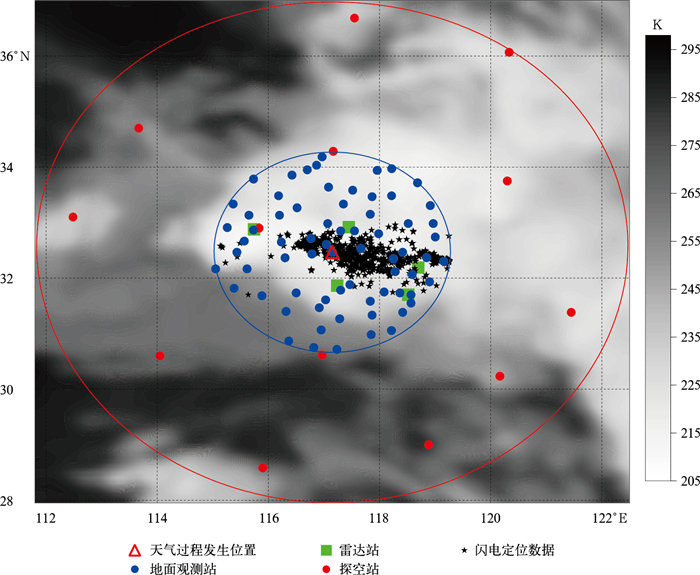
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: