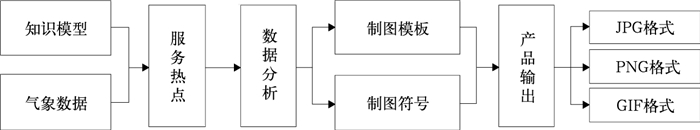
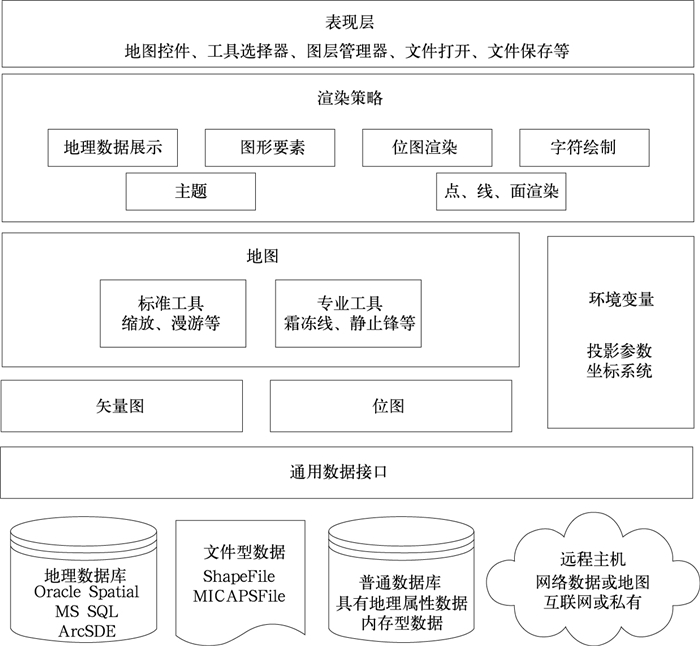
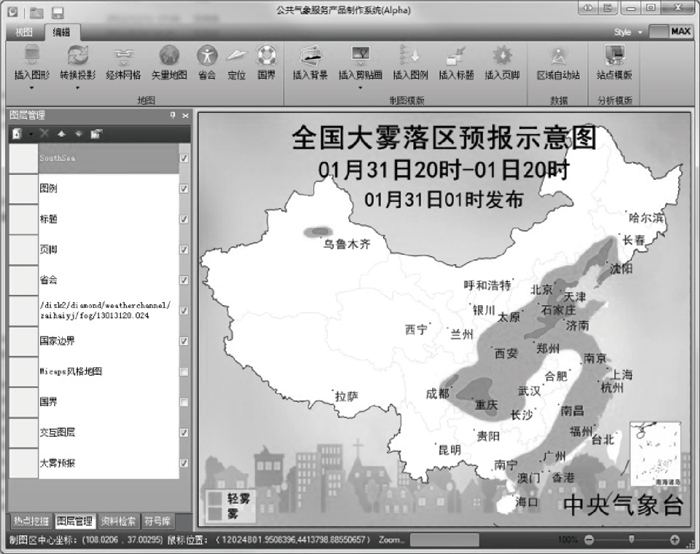
| 1级目录 | 2级目录 | 产品样式 | 后台数据 |
| 暴雨 | ① 降水情况——24 h累积降水量、实况暴雨区 ② 暴雨过程——逐小时降水累加动态 ③ 极值情况——突破极值城市排行 |
① 预警情况 ② 满足某阈值 (日降水量超过50 mm,100 mm,250 mm等) 的降水量实况排行 (34个省会级城市) ③ 单站当年第1场暴雨实况和预报 ④ 单站截至某时间的当年最大一场降雨 ⑤ 暴雨实况区的色域填图 ⑥ 暴雨实况累加动态图 ⑦ 降水突破极值情况 ⑧ 雷达动态示意 |
① 中央气象台预警 ② 预警服务提示 ③ 过去6 h,12 h,24 h降水量实况 ④ 地面观测实况数据 ⑤ 1~3 d降水量暴雨预报 ⑥ 历史降水资料 ⑦ 10 min雷达图 |
| 旅游天气 (端午节、高考等) |
① 适宜出行——温度满足某阈值,降水量低于某阈值 ② 不适宜出行——温度情况、降水情况、强风天气 ③ 有无灾害性天气预警 ④ 根据旅游特色作旅游推荐 |
① 未来1~3 d,1~7 d的无降水区域叠加图 ② 未来1~3 d,1~7 d的满足某阈值的最高、最低气温色域填图 ③ 未来1~3 d,1~7 d的大雨以上量级的叠加图 ④ 未来1~3 d,1~7 d的大雨以上量级的叠加图 ⑤ 未来1~3 d,1~7 d的大风以上量级的叠加图 ⑥ 未来1~3 d,1~7 d的降温幅度超过某阈值的叠加图 ⑦ 灾害预警的色域综合图 ⑧ 未来1~5 d的12 h,24 h天空云量色域填图 ⑨ 满足某温度阈值、某降水阈值、某风力阈值的综合色域填图 |
① 未来1~3 d短期天气预报 ② 中期天气预报 ③ 各类灾害性天气预警 ④ 1~5 d城市天气预报 (最高气温、最低气温、风力、降水等) |
| 农事服务 (夏收夏种) | ① 农作物生产情况 ② 影响农业的灾害性天气 ③ 高温、持续阴雨 ④ 寒露风 ⑤ 霜冻 |
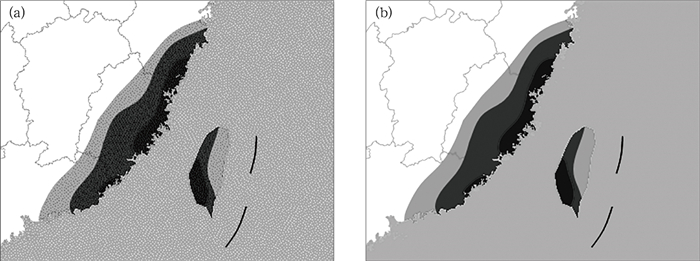
① 霜冻预报区域图 ② 寒露风的预报区域图 ③ 霜冻实况区域图 ④ 寒露风的实况区域图 ⑤ 满足某阈值 (突破35℃,40℃等) 的最高气温预报色域填图 ⑥ 满足某阈值的温度实况色域填图 ⑦ 连续低温阴雨的实况色域填图 ⑧ 大风区域实况、预报图 |
① 未来1~5 d最高气温、最低气温预报 ② 过去6 h,12 h,24 h降水量实况 ③ 地面观测实况数据 ④ 农作物生产情况 ⑤ 逐小时大风实况 |





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: