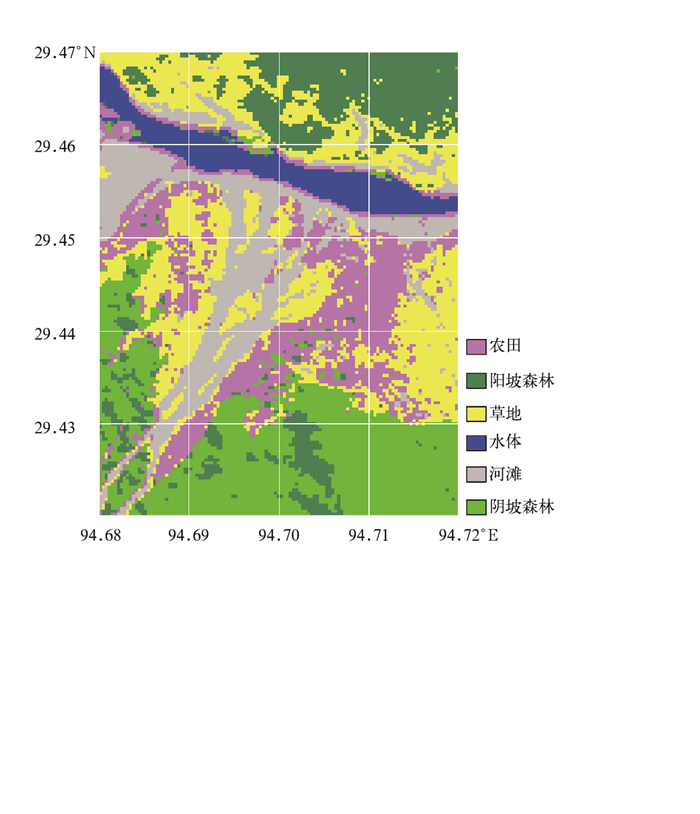
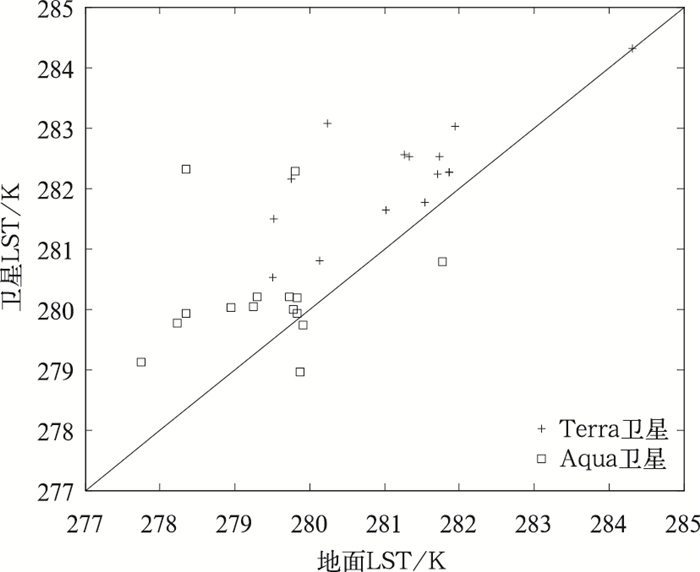
|
[1]
|
Wang W H, Liang S L, Meyers T.Validating MODIS land surface temperature products using long-term nighttime ground measurements.Remote Sens Environ, 2008, 112:623-635. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2007.05.024 |
|
[2]
|
|
|
[3]
|
|
|
[4]
|
Keramitsoglou I, Kiranoudis C T, Ceriola G, et al.Identification and analysis of urban surface temperature patterns in Greater Athens, Greece, using MODIS imagery.Remote Sens Environ, 2011, 115:3080-3090. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.06.014 |
|
[5]
|
Mildrexler D J, Zhao M S, Running S W.A global comparison between station air temperature and MODIS land surface temperature reveals the cooling role of forests.J Geophys Res, 2011, 116, G03025, doi: 10.1029/2010JG001486. |
|
[6]
|
Wang Y Y, Li X, Tang S H.Validation of the SEBS-derived sensible heat for FY3A/VIRR and TERRA/MODIS over an alpine grass region using LAS.International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2013, 23:226-233. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2012.09.005 |
|
[7]
|
|
|
[8]
|
|
|
[9]
|
|
|
[10]
|
Wan Z, Zhang Y, Zhang Q.Quality assessment and validation of the MODIS global land surface temperature.Inter J Remote Sens, 2004, 25:261-274. doi: 10.1080/0143116031000116417 |
|
[11]
|
Coll C, Caselles V, Galve J M, et al.Ground measurements for the validation of land surface temperatures derived from AATSR and MODIS data.Remote Sens Environ, 2005, 97:288-300. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2005.05.007 |
|
[12]
|
Wang K C, Liang S L.Evaluation of ASTER and MODIS land surface temperature and emissivity products using long-term surface longwave radiation observations at SURFRAD sites.Remote Sens Environ, 2009, 113:1556-1565. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2009.03.009 |
|
[13]
|
|
|
[14]
|
Liu Y B, Hiyama T, Yamaguchi Y.Scaling of land surface temperature using satellite data:A case examination on ASTER and MODIS products over a heterogeneous terrain area.Remote Sens Environ, 2006, 105:115-128. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2006.06.012 |
|
[15]
|
Guillevic P C, Privette J L, Coudert B.Land surface temperature product validation using NOAA's surface climate observation networks—Scaling methodology for the Visible Infrared Imager Radiometer Suite (VIIRS).Remote Sens Environ, 2012, 124:282-298. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.05.004 |
|
[16]
|
Wan Z, Dozier J.A generalized split-window algorithm for retrieving land surface temperature from space.IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34:892-905. doi: 10.1109/36.508406 |
|
[17]
|
|
|
[18]
|
Snyder W, Wan Z, Zhang Y, et al.Classification-based emissivity for land surface temperature measurement from space.International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1998, 19:2753-2774. doi: 10.1080/014311698214497 |
|
[19]
|
Li H, Sun D L, Yu Y Y, et al.Evaluation of the VIIRS and MODIS LST products in an arid area of Northwest China.Remote Sens Environ, 2014, 142:111-121. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.11.014 |
|
[20]
|
|
|
[21]
|
|
|
[22]
|
Jin M L, Liang S L.An improved land surface emissivity parameter for land surface models using global remote sensing observations.J Cliamte, 2006, 19:2867-2881. doi: 10.1175/JCLI3720.1 |
|
[23]
|
Wang K C, Wan Z M, Wang P C, et al.Estimation of surface long wave radiation and broadband emissivity using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) land surface temperature/emissivity products.J Geophys Res, 2005, 110, D11109, doi: 10.1029/2004JD005566. |
|
[24]
|
|
|
[25]
|
Vancutsem C, Ceccato P, Dinku T, et al.Evaluation of MODIS land surface temperature data to estimate air temperature in different ecosystem over Africa.Remote Sens Environ, 2010, 114:449-465. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2009.10.002 |





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: